Easy collaboration with fax notes
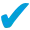 Add personal or team notes to any incoming or outgoing fax
Add personal or team notes to any incoming or outgoing fax Draw attention to specific sections that require focus or clarity
Draw attention to specific sections that require focus or clarity Share insights with your team directly on the fax
Share insights with your team directly on the fax
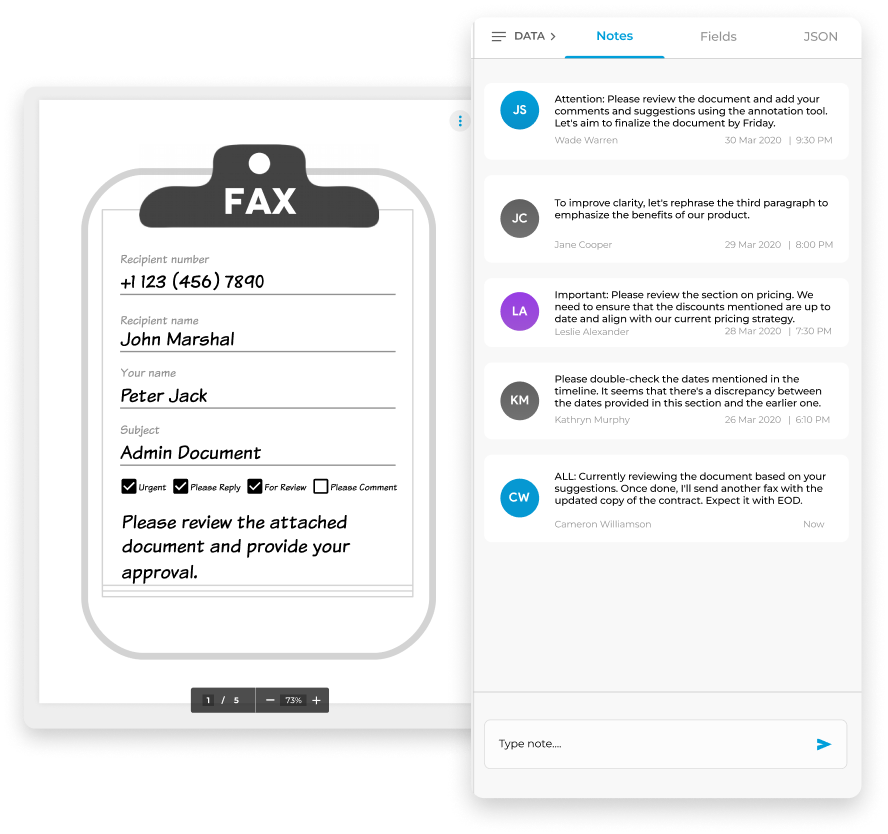
Enjoy iFax services at 50% off!
Your discount will be applied during checkout.

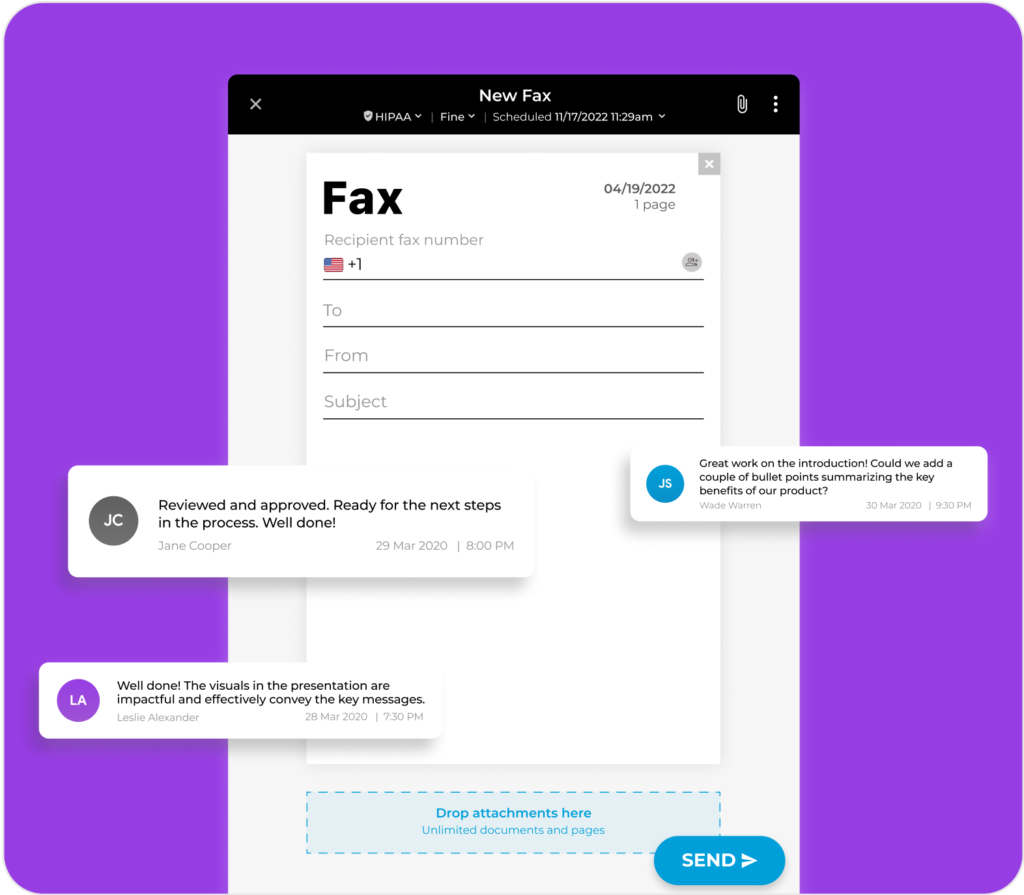
Elevate your document workflow by seamlessly integrating notes into both outgoing and incoming electronic faxes. These notes serve as valuable references, ensuring an organized approach and preventing the oversight of critical details.
Use these notes to prioritize tasks, collaborate with your team on fax documents, monitor document progression, and highlight the status of essential fax-related activities.
Fax Notes enhances communication and team collaboration and, at the same time, improves workflow efficiency.
Here’s how to add document notes to a fax on iFax:
That’s it.
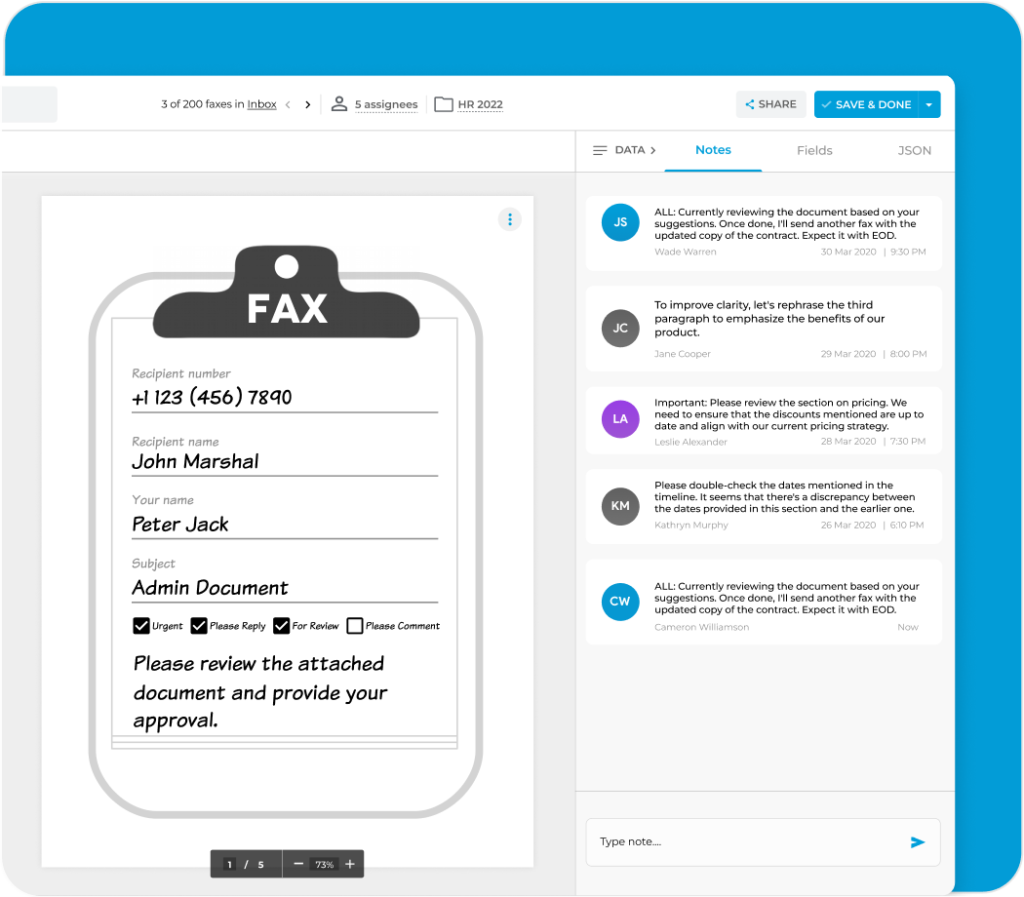
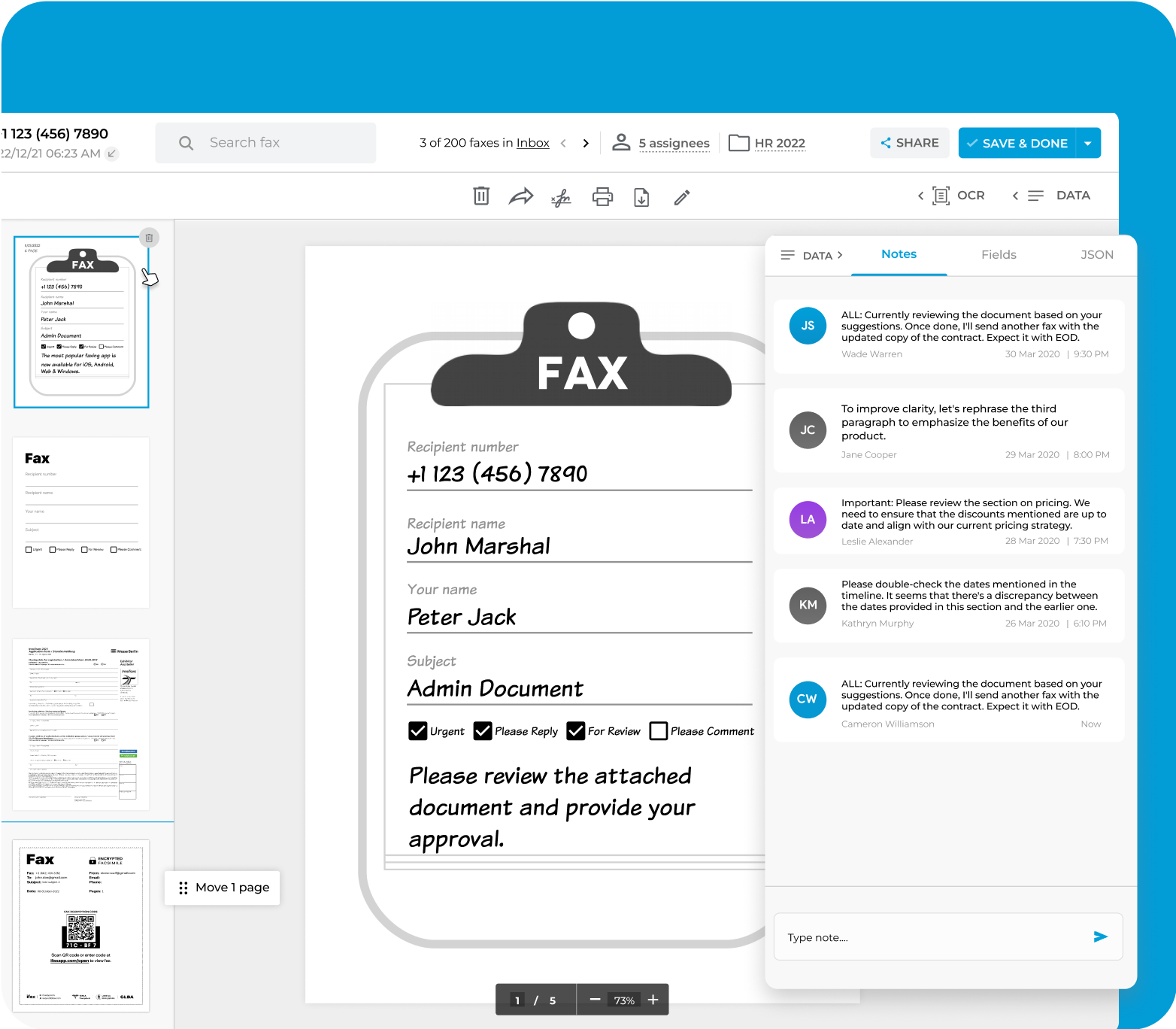
iFax eliminates the need for external note-taking tools or separate documents, saving you valuable time and effort in searching for relevant details within the fax.
Adding fax notes boosts how you engage with your documents. You can highlight priorities, add context, and take action with clarity. Try iFax for free to see how these features can significantly improve your workflow.